hello friends! new(ish)!
Build a PC: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
>85x No edit summary |
>85x |
||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
|- align="center" | |- align="center" | ||
|Commonly used for fans and older drives. || Used for graphics cards.<br />According to the ATX specification, it should not transmit more than 75W. || Also used for graphics cards, but can (should) output up to 150W. || Used as the motherboard's main power source.<br />Always plug in both parts. || Used as the motherboard's secondary power source, but still required for the motherboard to work.<br />When using 8 pins, it's called the EPS connector, but if only using 4 pins, it's ATX12V. || The Serial ATA power connector is used for hard drives, SSDs and optical drives. || An obsolete connector, used for powering floppy drives. | |Commonly used for fans and older drives. || Used for graphics cards.<br />According to the ATX specification, it should not transmit more than 75W. || Also used for graphics cards, but can (should) output up to 150W. || Used as the motherboard's main power source.<br />Always plug in both parts. || Used as the motherboard's secondary power source, but still required for the motherboard to work.<br />When using 8 pins, it's called the EPS connector, but if only using 4 pins, it's ATX12V. || The Serial ATA power connector is used for hard drives, SSDs and optical drives. || An obsolete connector, used for powering floppy drives. | ||
|} | |||
=== PSU Efficiency === | |||
The higher the power supply's efficiency is, the less energy it's going to convert to heat, and therefore, run cooler. | |||
The standard for measuring efficiency is 80Plus, requiring tests at 10% (Only Titanium), 20%, 50% and 100% of rated load at both 115V and 230V. | |||
== Efficiency level certifications == | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! 80 Plus test type | |||
! colspan="4" | 115V internal non-redundant | |||
! colspan="4" | 230V internal redundant | |||
|- | |||
! Percentage of rated load | |||
! 10% | |||
! 20% | |||
! 50% | |||
! 100% | |||
! 10% | |||
! 20% | |||
! 50% | |||
! 100% | |||
|- | |||
| 80 Plus | |||
| | |||
| 80% | |||
| 80% | |||
| 80% | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| 80 Plus Bronze | |||
| | |||
| 82% | |||
| 85% | |||
| 82% | |||
| | |||
| 81% | |||
| 85% | |||
| 81% | |||
|- | |||
| 80 Plus Silver | |||
| | |||
| 85% | |||
| 88% | |||
| 85% | |||
| | |||
| 85% | |||
| 89% | |||
| 85% | |||
|- | |||
| 80 Plus Gold | |||
| | |||
| 87% | |||
| 90% | |||
| 87% | |||
| | |||
| 88% | |||
| 92% | |||
| 88% | |||
|- | |||
| 80 Plus Platinum | |||
| | |||
| 90% | |||
| 92% | |||
| 89% | |||
| | |||
| 90% | |||
| 94% | |||
| 91% | |||
|- | |||
| 80 Plus Titanium | |||
| 90% | |||
| 92% | |||
| 94% | |||
| 90% | |||
| 90% | |||
| 94% | |||
| 96% | |||
| 91% | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 13:32, 29 January 2014
Building a desktop
Building your own desktop allows for greater customisation and control. It's worth it even though it's harder.
Some common issues when building your PC
- Use standoffs under the motherboard mounting holes!
- Read the manual that came with your motherboard.
- Plug in all the power connectors.
- If you have a graphics card, connect your monitor to your graphics card and NOT to the motherboard
- Spread thermal paste however you feel like, use about half a pea size amount, if using the stock heatsink don't touch the preapplied stuff
- Install the CPU heatsink before putting the motherboard into the case, unless it's a water cooling setup.
- The CPU socket lever on Intel motherboards will be hard to push down and feel like it's taking too much force. That's normal.
Power supplies
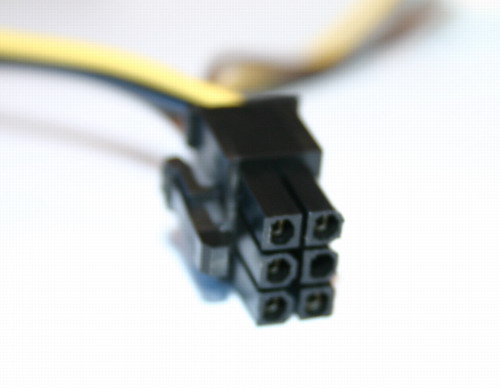
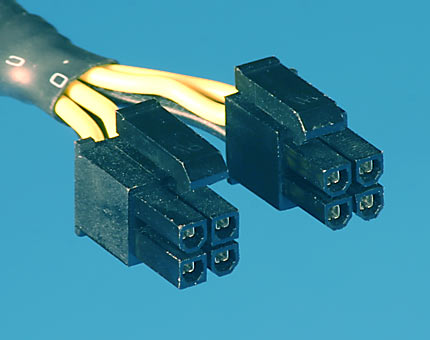
Common power connectors and their usage
| 4-pin molex | 6-pin PCI-E | 6+2-pin PCI-E | 20+4-pin ATX | 4+4-pin ATX12V/EPS | 15-pin SATA | 4-pin floppy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commonly used for fans and older drives. | Used for graphics cards. According to the ATX specification, it should not transmit more than 75W. |
Also used for graphics cards, but can (should) output up to 150W. | Used as the motherboard's main power source. Always plug in both parts. |
Used as the motherboard's secondary power source, but still required for the motherboard to work. When using 8 pins, it's called the EPS connector, but if only using 4 pins, it's ATX12V. |
The Serial ATA power connector is used for hard drives, SSDs and optical drives. | An obsolete connector, used for powering floppy drives. |
PSU Efficiency
The higher the power supply's efficiency is, the less energy it's going to convert to heat, and therefore, run cooler. The standard for measuring efficiency is 80Plus, requiring tests at 10% (Only Titanium), 20%, 50% and 100% of rated load at both 115V and 230V.
Efficiency level certifications
| 80 Plus test type | 115V internal non-redundant | 230V internal redundant | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage of rated load | 10% | 20% | 50% | 100% | 10% | 20% | 50% | 100% |
| 80 Plus | 80% | 80% | 80% | |||||
| 80 Plus Bronze | 82% | 85% | 82% | 81% | 85% | 81% | ||
| 80 Plus Silver | 85% | 88% | 85% | 85% | 89% | 85% | ||
| 80 Plus Gold | 87% | 90% | 87% | 88% | 92% | 88% | ||
| 80 Plus Platinum | 90% | 92% | 89% | 90% | 94% | 91% | ||
| 80 Plus Titanium | 90% | 92% | 94% | 90% | 90% | 94% | 96% | 91% |
External Links
- PCPartPicker - Computer component aggregator and comparison tool dedicated to picking out compatible computer components, allowing one to seamlessly create a desktop.
- Logical Increments - Formerly known as the "Falcon Guide", a good starting point to building a computer on a budget, components are grouped by price point.
- ChooseMyPC.net - Cookie cutter PC build generator, also hosts several guides and resources related to builds.