hello friends! new(ish)!
Passwords: Difference between revisions
>Linuks m Added KeePassXC to list of password managers. |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== How passwords are compromised == | == How passwords are compromised == | ||
Passwords are mostly compromised offline by breaking a password's hash. Every few months some huge website with millions of users will get owned and it's [[Databases | database]] of hashed passwords will be made public. The biggest database so far is the [ | Passwords are mostly compromised offline by breaking a password's hash. Every few months some huge website with millions of users will get owned and it's [[Databases |database]] of hashed passwords will be [https://haveibeenpwned.com/ made public]. The biggest database so far is the [https://archive.is/54HFw RockYou] database. | ||
Crackers will run their tools against the hashed passwords to unmask them. From this they will learn: | Crackers will run their tools against the hashed passwords to unmask them. From this they will learn: | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
* Add numbers to the end of words. | * Add numbers to the end of words. | ||
* Add symbols before/after/between words. | * Add symbols before/after/between words. | ||
* Turn the words into l337 sp34k. | * Turn the words into l337 sp34k (Very well known by this point). | ||
* Add the website's name onto the end of your password. | * Add the website's name onto the end of your password. | ||
* Use common phrases like 1pledgeallegiancetotheflag or yippiekiyaymotherfucker. | * Use common phrases like 1pledgeallegiancetotheflag or yippiekiyaymotherfucker. | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== Choosing a good password == | == Choosing a good password == | ||
[[File:Password strength xkcd 936.png|thumb|432x432px|A graphical example of the Diceware method, courtesy of [https://xkcd.com/936/ xkcd]]] | |||
There are two types of passwords: | There are two types of passwords: | ||
* Regular passwords, which you keep in a password manager. | * Regular passwords, which you keep in a password manager. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 27: | ||
The best passphrases are generated with [http://world.std.com/~reinhold/diceware.html Diceware] which involves rolling 6 sided die to select random words which build a long cryptographically random passphrase. This produces passphrases [https://firstlook.org/theintercept/2015/03/26/passphrases-can-memorize-attackers-cant-guess/ you can memorise, but attackers can't guess] (easily). | The best passphrases are generated with [http://world.std.com/~reinhold/diceware.html Diceware] which involves rolling 6 sided die to select random words which build a long cryptographically random passphrase. This produces passphrases [https://firstlook.org/theintercept/2015/03/26/passphrases-can-memorize-attackers-cant-guess/ you can memorise, but attackers can't guess] (easily). | ||
The rest of your passwords, most of which will be for websites, should be generated | The rest of your passwords, most of which will be for websites, should be generated and stored by your password manager. | ||
=== Password managers === | === Password managers === | ||
These are programs which will generate long, random passwords using the full character set. Passwords which can only be broken by brute force, which can take longer than all the time since the [[Astronomy | big bang]]. You can easily have different passwords for every site you visit and set password expiry dates to remind you to change your passwords every so often (yearly? 6 monthly?). Passwords are kept within an offline encrypted database which you should | These are programs which will generate long, random passwords using the full character set. Passwords which can only be broken by brute force, which can take longer than all the time since the [[Astronomy |big bang]]. You can easily have different passwords for every site you visit and set password expiry dates to remind you to change your passwords every so often (yearly? 6 monthly?). Passwords are kept within an offline encrypted database which you should [[Backups|back up]] regularly. | ||
Good password managers: | Good password managers: | ||
* [https://keepassxc.org/ KeePassXC] | * [https://keepassxc.org/ KeePassXC] | ||
* [https:// | * [https://bitwarden.com/ Bitwarden (self-hosted)] | ||
* [ | * [https://psono.com/ Psono] | ||
* [ | * [https://strongboxsafe.com/ Strongbox] | ||
Some password managers store your passwords in the cloud, making them a colossal target for hackers and placing your trust in the the skills of the cheapest admin the cloud can afford. Don't use them. Examples include LastPass and 1Password. | Some password managers store your passwords in the cloud, making them a colossal target for hackers and placing your trust in the the skills of the cheapest admin the cloud can afford. Don't use them. Examples include LastPass and 1Password. | ||
| Line 61: | Line 59: | ||
* Some other strategy you thought of five minutes ago: The people who write password managers have already thought of it and determined why it is less secure than what they already use. | * Some other strategy you thought of five minutes ago: The people who write password managers have already thought of it and determined why it is less secure than what they already use. | ||
If you're skeptical at all about how advanced password crackers are, [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DTbCjpsdhfM UNHash] is a talk from late | If you're skeptical at all about how advanced password crackers are, [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DTbCjpsdhfM UNHash] is a talk from late 2019 explaining the current state of password cracking. | ||
[[Category:HowTo]] | [[Category:HowTo]] | ||
[[Category:Recommendations]] | [[Category:Recommendations]] | ||
[[Category:Security]] | [[Category:Security]] | ||
Revision as of 00:46, 8 December 2024
How passwords are compromised
Passwords are mostly compromised offline by breaking a password's hash. Every few months some huge website with millions of users will get owned and it's database of hashed passwords will be made public. The biggest database so far is the RockYou database.
Crackers will run their tools against the hashed passwords to unmask them. From this they will learn:
- What the most common passwords are.
- What strategies people use to try and harden their passwords (e.g. adding numbers to the end).
- How often unique passwords are used (0.0001% of the time).
Once the passwords in the hashed password database are unmasked, crackers have an accurate view of how people choose passwords and therefore have a better chance of cracking your password.
A common technique is a dictionary attack, which will try every entry in a customized word list ("dictionary"). This might be the Oxford English Dictionary or every word which came up in the first 10 pages of a google search for "memes". Advanced dictionary attacks will do all that shit you thought you were so clever for thinking of:
- Use multiple words.
- Add numbers to the end of words.
- Add symbols before/after/between words.
- Turn the words into l337 sp34k (Very well known by this point).
- Add the website's name onto the end of your password.
- Use common phrases like 1pledgeallegiancetotheflag or yippiekiyaymotherfucker.
- Much, much more, guessing billions of times per second.
Choosing a good password
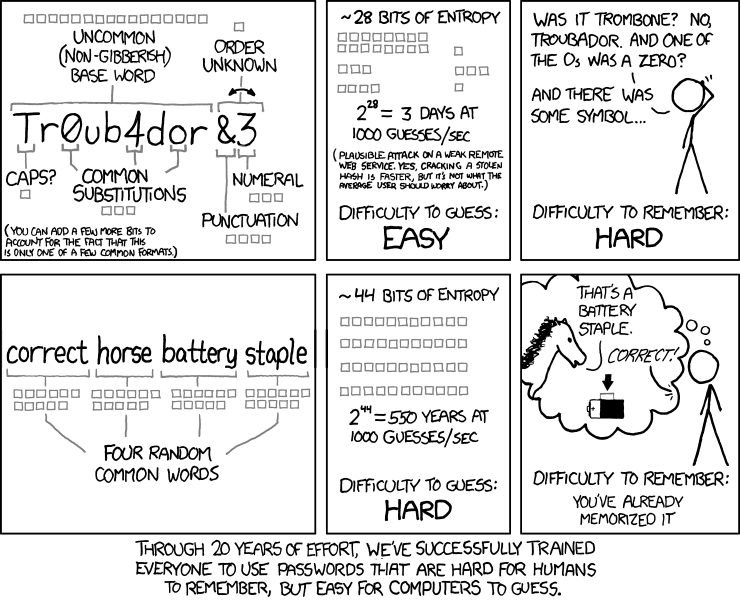
There are two types of passwords:
- Regular passwords, which you keep in a password manager.
- Passphrases, longer strings that are used at the most important places, for example to protect your password manager database or unlock your encrypted disk.
The best passphrases are generated with Diceware which involves rolling 6 sided die to select random words which build a long cryptographically random passphrase. This produces passphrases you can memorise, but attackers can't guess (easily).
The rest of your passwords, most of which will be for websites, should be generated and stored by your password manager.
Password managers
These are programs which will generate long, random passwords using the full character set. Passwords which can only be broken by brute force, which can take longer than all the time since the big bang. You can easily have different passwords for every site you visit and set password expiry dates to remind you to change your passwords every so often (yearly? 6 monthly?). Passwords are kept within an offline encrypted database which you should back up regularly.
Good password managers:
Some password managers store your passwords in the cloud, making them a colossal target for hackers and placing your trust in the the skills of the cheapest admin the cloud can afford. Don't use them. Examples include LastPass and 1Password.
Bad Password Strategies
Don't do this:
- Less than 10 characters.
- Lowercase only.
- Dictionary words.
- Names, sports teams, pet names, chinese cartoon references.
- "B-But my password had both letters and numbers!"
Or this:
- Using the same password in two (or more) different places.
- Using the same password with slight changes for each place it's used.
- Using a password you've ever shared with anyone ever.
I'm so clever I trolled myself shit:
- Hashing a word/phrase: This may get you a decent password length, but if you're going to use a tool, why not use a tool specific to making good passwords?
- Some other strategy you thought of five minutes ago: The people who write password managers have already thought of it and determined why it is less secure than what they already use.
If you're skeptical at all about how advanced password crackers are, UNHash is a talk from late 2019 explaining the current state of password cracking.