hello friends! new(ish)!
GNU/Linux
A number of Distro pages redirect here. For individual Distros, see Recommended GNU/Linux Distributions, and see if they have their own pages as well

Linux at its core is a kernel, the central driving force of an operating system that allocates resources to other aspects of the system. Linux, along with the GNU system (which is closely associated with the Free Software Foundation) are now collectively referred to as GNU/Linux, and make up a complete operating system which is widely used today by millions across the world. To read more about the history of the GNU project and Linux, see this article.
Why use GNU/Linux?
The free software philosophy is about an open and shared operating system which is not only free as in money, but free as in freedom. The GNU/Linux system gives users more control over their computing experience than competing operating systems such as Windows, which could contain malicious features without the user's knowledge.
What's all this about distributions?
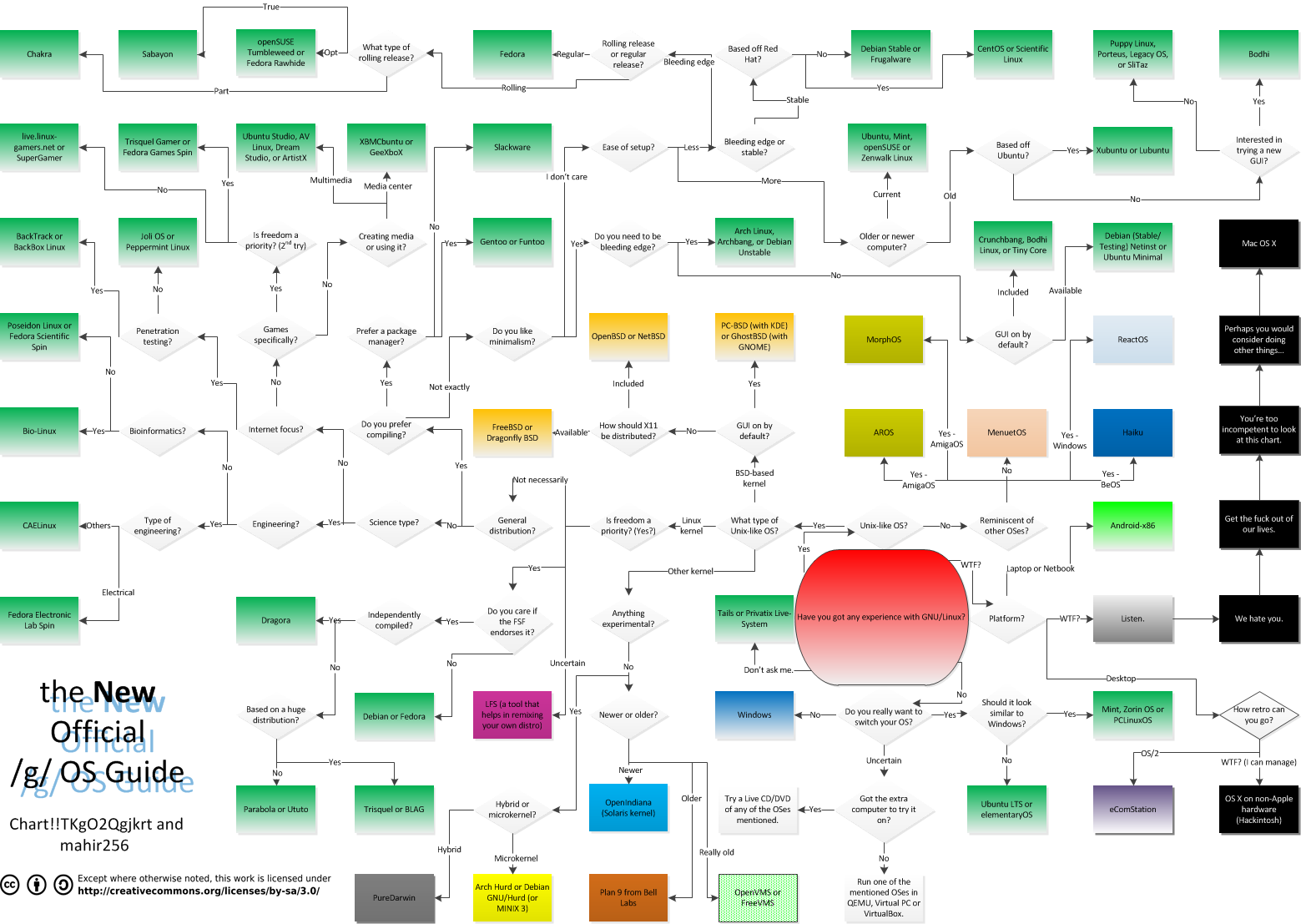
There are a lot of GNU/Linux distributions, also known as distros.
Most distros are at least somewhat similar with each other. The main differences are between the init system, package manager (and the repositories it has access to), desktop environment, (bloat) and default configurations. Most distros have their own little niche. Some are FSF compatible (or almost), for ricing, for getting shit done or just because you hate yourself or just love pain (Arch/Gentoo). Always at least try another distro before saying that you hate it. You will find that all of them have their own qualities.
When choosing a distro, keep some things in mind. Linux is about choice. There are stable and rolling distributions. Some stable distros can be made rolling by selecting the proper repositories and vice versa. Some are semi-rolling, they release snapshots of packages. Stable is best for beginners and rolling is best for developers and advanced users who want the latest and greatest.
Almost every distro can be riced by setting up the right DE and/or WM. DEs can be tiling or stacking.
Recommended Distributions
See also: Babbies First Linux
These are various distros that are recommended by people on /g/ and /tech/. Distrowatch is a good resource for discovering new Linux distributions.
Debian-based
These Linux distributions are descended from Debian GNU/Linux and typically use the .deb package format and the APT package manager.

|
Debian GNU/Linux
Pros
Cons
|

|
Linux Mint
Pros
Cons
|
|
Ubuntu
Pros
Cons
|
RPM-based
These distributions utilize RPM packages, and stemming from the success of Red Hat Enterprise Linux, tend to be more business-oriented than the community-driven Debian.

|
Fedora
Pros
Cons
|

|
CentOS
Pros
Cons
|

|
openSUSE
Pros
Cons
|
User-centric
These distributions are designed for the purpose of giving the user control of their operating system. They are significantly harder to get into than those mentioned previously.

|
Gentoo
Pros
Cons
|
| CRUX
Pros
Cons
|

|
Slackware
Pros
Cons
|
Note: The following distributions are based on Arch Linux, though they are not user-centric per the criteria above.

|
Arch
Pros
Cons
|

|
Manjaro
Pros
Cons
|

|
Antergos
Pros
Cons
|
Stallman-style Free distros
The GNU Project maintain their own list of recommended distros that they deem 'free', as in completely devoid of nonfree software. That list can be found here.
Installation
Virtual Machines
If you are not ready to commit to installing a GNU/Linux system, you may want to try one out in a virtual environment first.
Making a Bootable USB Installer
In addition to installing from CD, you can also install from a USB flash drive. A USB installer created using the following steps should work with both BIOS and UEFI systems. However, for UEFI systems you may need to disable "Secure Boot" in the UEFI configuration panel. For UEFI support your flash drive MUST be formatted as fat32 (also called vfat in GNU/Linux) when attempting to boot from it.
- Download the disk image of your chosen distribution.
- Verify the integrity of the download if a checksum is provided.
- Use the image tool recommended in your distribution's install notes to copy the iso to your USB-drive and make it bootable. Note: There are many universal tools available, but they do not always work correctly for all distributions. Some of them include:
GNOME Disk Utility Method
Any Linux distribution running GNOME can easily make a bootable USB drive through nautilus and gnome-disk-utility. Just right click your downloaded .iso file and select "Open with Disk Image Writer." Make sure you don't need any of the data on the USB stick! When GNOME Disk Utility opens, pick the flash drive from the "Destination" drop down menu and click "Start Restoring."
Manual Terminal Method
- This method requires you are already running Linux and have an iso specifically crafted for USB drives or a "hybrid" CD/USB image. Most distributions will mention the type of iso on their download page.
- Using the commands lsblk or fdisk -l( as exemplified bellow), find what [drive letter] is the letter of your removable device. Please note that it is the device (e.g. /dev/sdb), and not the partition number (e.g. /dev/sdb1).
fdisk -l
WARNING!!!
- The dd command is also known as "Disk Destroyer" because it is very easy to annihilate the data on a device unintentionally.
- Make absolutely sure that "of=/dev/sd[drive letter]" is the correct device!
- Now use run dd to install the iso in your device of choice.
dd bs=4M if=[/path/to/distro.iso] of=/dev/sd[drive letter]
An example of using the dd command could be:
dd bs=4M if='/home/moot/Downloads/debian-7.3.0-amd64-netinst.iso' of=/dev/sdb
Remember that to use " " if you path contains spaces.
- Last, wait patiently until the command has executed. No outputs will be printed until the process is finished. You can check progress of a dd command by finding the process ID with ps aux | grep dd and issuing the kill -s USR1 <pid> command against it. Just don't forget the USR1 signal or you will terminate the process.
GNU/Linux Naming Controversy
The GNU/Linux naming controversy is a dispute regarding whether or not to refer to the operating system commonly known as Linux as GNU/Linux. GNU/Linux was a term originally created by the Free Software Foundation to refer to the combination of the GNU corelibs and the Linux Kernel, which they argued to form a functioning operating system. The Free Software Foundation recommends the term GNU/Linux because it argues the GNU project was part of a project to develop an operating system, from which the kernel was the last piece to complete (see GNU Hurd). The Free Software Foundation suggests that the inclusion of the term GNU in the operating system’s name would recognize their contribution and their free software ideals ("Free Software as a Social Movement". ZNet.). Richard M. Stallman writes:
Today tens of millions of users are using an operating system that was developed so they could have freedom—but they don't know this, because they think the system is Linux and that it was developed by a student 'just for fun'.
On the opposite side of the argument, Linux supporters argue that the contribution of the Free Software Foundation is minimal (for example, GNU components make up only 8% of Ubuntu). Eric S. Raymond writes:
Some people object that the name "Linux" should be used to refer only to the kernel, not the entire operating system. This claim is a proxy for an underlying territorial dispute; people who insist on the term GNU/Linux want the FSF to get most of the credit for Linux because [Stallman] and friends wrote many of its user-level tools. Neither this theory nor the term GNU/Linux has gained more than minority acceptance.
Linux proponents also argue that since the operating system is often referred to as Linux by the mainstream media and most users, that it should be used as such, as opposed to GNU/Linux.
Let's Learn About GNU/Linux
The Terminal
The terminal, also known as the Command Line, Shell, or just cold, emotionless text on a black background, gives you access to the real power and beating heart of Linux. Linux by default uses BASH, or Bourne-Again Shell which is based on the shell program `sh' from UNIX, written by Steven Bourne of Bell Labs. Bash will be all of our terminal interaction.
To manage multiple user sessions on a single machine, Linux (and UNIX) uses what is called a TeleTYpeWriter (TTY) for each user to interface with the main kernel. Each tty is handled by its own special device file, located in the directory /dev. It also uses Pseudo Terminal Slave (pts) to handle other types of terminal interface, but this is beyond the scope of this guide.
You may be wondering what the difference between shell and TTY is. Shell is the command interpreter that runs everything you type in, and TTY is the connection that handles the data between Linux and the shell.
The shell uses files called stdout, stdin and stderr to handle text input and output to and from programs.
- stdin - Standard Input - All your typed text input goes into programs through here.
- stdout - Standard Output - All successful program output goes to here.
- stderr - Standard Error - All error messages and problem codes go to here.
You should get familiar with the man pages, which are essentially the manual, and will display help pages on almost all commands.
Usage: man COMMAND
Where COMMAND is replaced with whatever command you want help on. Press 'q' to exit a manual page. Alternatively, most commands will allow you to add --help on the end to get their own personal help pages.
Every key pressed sends a character to the terminal and you can send different characters by holding down keys like [Ctrl] or [Alt]. This is how the shell can tell what key is pressed, and thus, allow shortcuts to be defined. Some of the more useful keyboard shortcuts are defined:
- Up arrow or Down arrow - Scroll through typed commands
- Shift + Page Up or Page Down - Scroll up or down through shell output
- Home or End - Move to the start or end of a line, respectively
- Tab - Autocomplete a file name, directory name or command name.
- Ctrl + C - End a running process
- Ctrl + D - End-Of-File (EOF) character (usually ends a process or signifies the end of input data)
- Ctrl + Z - Send the currently running process to the background
- Ctrl + L - Clear the screen, same as running the clear command
If you're using BASH as your shell (most distros default to this) you can customize it to your liking.
Common Commands
- pwd - Print Working Directory. Outputs the full path of the current directory.
- cd - Change Directory. Used to switch to a different directory.
- ls - List. Lists files and directories in the current directory.
- ls -a Lists "hidden" files and directories also. Hidden files in linux are preceded with a full stop.
- ls -l Lists further information about the files, including size, modify date, owner and permissions.
- ls -t List by modify date, with the most recently modified files at the top.
- cp - Copy a file/directory.
- cp -r Descend into directories (recursively copy all directory contents).
- mv - Move or rename a file.
- rm - Delete a file.
- rm -r Delete directory contents. (Never rm -r /)
- chmod - Changes file permissions for the Owner, Group and Others.
- chown - Changes the owner of a file.
- chgrp - Changes the group of a file.
- date - Display current date and time.
- who - Displays a list of currently logged in users.
- echo - Prints to stdout.
- cat - Concatenates text to stdout.
- grep - Searches for strings in a file or stdin.
- su - Switch user. Defaults to root.
- sudo - Similar to
subut uses your own password instead. Lets you configure access in/etc/sudoers. - passwd - Change password. Defaults to current account.
- rsync - Synchronizes files and directories.
- halt - halt the system
- halt -p - also shut off the power
- systemctl - Interface to SystemD.
- systemctl poweroff - Shutdown.
- systemctl reboot - Reboot.
- systemctl start <service> Start a service.
- systemctl stop <service> Stop a service.
- journalctl - Interface to SystemD logging.
Piping and redirection
There are a number of little quirks that the shell has that gives it more functionality. Piping takes the stdout of the left program and connects it (i.e. pipes it) into stdin of the right program with the pipe operator.
For example:
# Count number of words in helloworld.txt cat helloworld.txt | wc -w
Redirection directs data in and out of files, i.e.
# Redirect stdout to file echo "Hello world" > helloworld.txt # Redirect stdout to the end of a file echo "world." >> hello.txt # Redirect a file to stdin more < helloworld.txt
Kernel
The kernel is the central nervous system of an operating system. Luckily, The Linux kernel is still maintained by Linus Torvalds. Find out about the version, kernel hacking and security on kernel.org.
Useful links regarding command-line
- Linux Command explains the shell, indispensable to users who want to take full advantage of GNU/Linux distributions.
- Commandlinefu provides a fun experience while offering a lot of useful command-line gems making it a great site to explore and learn more about the command line.
External Resources
- Videos
See Also
FSF - The Free Software Foundation